Digital Marketing Mumbo Jumbo
If you are like me, you’ve been hammered recently with messaging about new forms of marketing like “neuromarketing” or terms like “behavioral marketing” “Renaissance marketing”, and of course all this under the umbrella of AI. I also read somewhere that if you want to market in Silicon Valley you must have a “scientific approach”. Lots of interesting read I am sure but also lots of mumbo jumbo stuff.
Bottom line, everyone is talking about understanding the customer, showing the right ad at just the right time, people’s behavior, brand, analytics, etc. And while all this is great and valuable, I wonder if we are not getting lost deep in the science and analytic, and loosing track of what, at its core, marketing is all about.
By doing a simple search on marketing techniques, I came up with some simple explanation that reads “for all its complexity, at its core, marketing revolves around the basic principles of the 7 P’s (Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Process, Physical Evidence). There are other variations of these famous 7 Ps but these are the most common ones that I know.”
I found this one on Assemblo (assemblo.com). While this is not exactly exciting stuff to read and maybe obvious to some these are basic principles worth reading.
The 7 Ps (assemblo.com)
Back in the 1960s, when marketing men smoked at their desks, ladies tapped away in their typing pools, and sliced bread was the yardstick of whether a product was any good, a marketing notion was hatched that was so perfect, sixty years later it is still considered an integral part of any marketing strategy.
It’s called the seven Ps of marketing and includes product, price, promotion, place, people, process, and physical evidence.
Here’s how the 7 Ps of marketing can be applied to everything in your marketing mix:
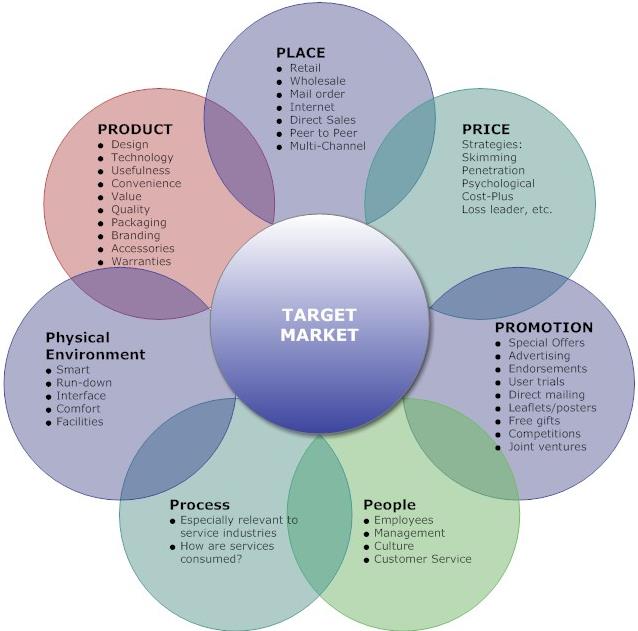
- PRODUCT
It goes without saying that the service or product you’re selling should be at the center of every element of the marketing mix.
Fundamentally, it allows you to address the questions key to sales conversion: what problem or issue does the product solve for customers? Why is your product the best one to solve it?
The digital marketing mix is perfect for showcasing your products, through SEO, blogs or articles, paid advertising, influencer marketing, and viral video campaigns, for example.
- PRICE
The strategy behind the pricing of your product needs to be based on what your customers are prepared to pay, costs such as retail mark-up and manufacturing, as well as other considerations.
Your marketing mix can include subscription and membership discounting programs, or email marketing of promotions and sales.
- PROMOTION
Successful marketing strategies include all the promotional activities across the marketing mix, including advertising, direct marketing, and in-store promotional activities.
The possibilities of digital promotion are limited only by your imagination and can include online events, chats, social media groups, and livestreams.
- PLACE
Where and how your product is displayed and sold should be directly informed by your customers.
A deep understanding of their purchasing patterns – and targeting them at the right stage in their buying cycle – will make it clear where you should promote and sell your products and how that fits into your online and real-world marketing mix.
7-Ps-of-Marketing-infographic_960x540
- PEOPLE
Excellent customer service not only converts to sales but can increase your customer base by referrals. Acquiring these referrals by people who love your brand can also be a great example of how your marketing efforts can support your sales process.
It’s important that everyone who represents your brand or deals with customers – including the non-human chat bot variety! – are fully trained sales professionals with an intimate knowledge of your product and how it will improve the lives or solve the problems of your customers.
- PROCESS
The process of delivering your product to the consumer should be designed for maximum efficiency and reliability but may also include features that are in line with your brand, such as being environmentally or sustainably focused.
With the rise in online shopping, digital partnerships and logistics have become an essential part of the marketing mix.
- PHYSICAL EVIDENCE
Physical evidence incorporates aspects that proves your brand exists and that a purchase took place.
Examples of proof that your brand exists can include things like a physical store or office for your business, a website if your business operates solely online, and printed business cards that you exchange when meeting people. Examples of proof of purchases can include physical or digital receipts, invoices, or follow-up email newsletters that you send to customers as a retention exercise.
They Conclude with the following:
Your marketing mix must also take into consideration all the things your customer sees, hears – sometimes even smells – in relation to your product or service.
This, of course, includes packaging and branding, but should also bring in the ways products are displayed in stores, where they are placed, and the context in which they sit, as well as digital placement, including on your website and social media.
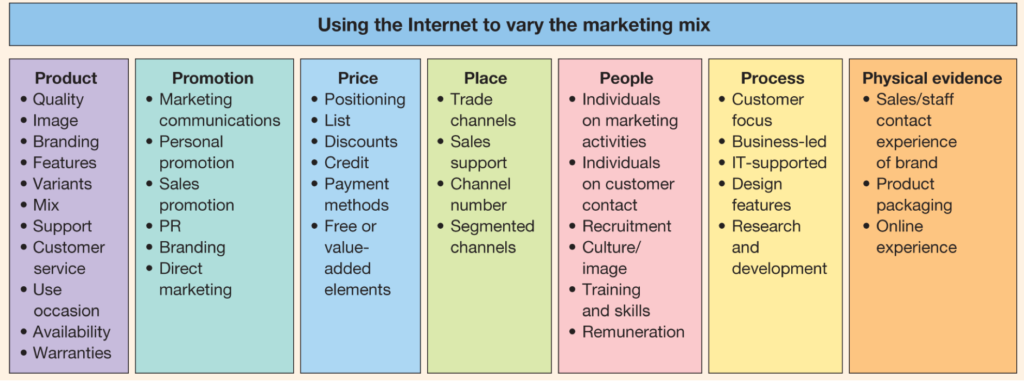
I found another explanation of the 7 Ps on an Australian government website, and you can review it below in the notes and resources. However, the bottom line is that the 7 Ps are a list of very LOGICAL and straight forward principles that MUST be understood, analyzed, and applied to succeed in pretty much any business.
Some people will inevitably tell me that online/digital marketing is a completely different ball game and that we must look at it with a more “technical” or “scientific” mind. Analytic, A/B testing, etc. are key to the success of any campaign.
Sure, that make perfectly good sense. However, how does it differ from a store putting candies and cool drinks near the cashier line? They analyzed their customers habits and tested different products (A/B) and feature what worked. What about the 40% coupons the CVS sends constantly to their customers, or the BOGO offers that you see everywhere. I doubt that they used google analytics or complex scientific research to make evident what works. But wait a min. What did they do and why is it working? Well, simply put THEY OBSERVED THEIR CUSTOMERS AND LISTEN TO THEM, MADE NOTES OF THESE PEOPLE’S NEEDS OR SOCIAL CHANGES AND ADAPTED. Take the examples of a venerable stores like 7Eleven offering more junk stuff to attract younger customers. How about Dunken Donuts promoting and branding their coffee? Gas Stations turning into mini malls and food courts? McDonald offering salad bar. These companies found a way to adapt to better service their customers’ needs based on trends, changes in life style, etc.
So, let’s review what is so different about digital marketing. A quick search with the search criteria “What is digital marketing” reveals the following: “Digital marketing is the act of selling products and services through channels such as social media, SEO, email, and mobile apps. Basically, digital marketing is any form of marketing that involves electronic devices.”
Wow. I am blown away. Something revolutionary here. We are selling but this time via some type of digital mean. As a matter of fact, I would say that there are many more options and found the following list:
- Social Media Marketing Platforms
- Influencer Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Content Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Marketing
- Pay-per-click (PPC)
- Affiliate Marketing
- Mobile Marketing
Source: marketingevolution.com
To These, I would add the following
- Search Marketing (SEM)
- PR (online)
- Blogs
- Newsletter Marketing
And just in case this is not enough, we can also add Marketing Automation just to satisfy the purists who classify this under its own “umbrella” of marketing.
To these you need to also add all the devices that plug in to the NET and these would include computers and laptop, smart phones, tablets, interactive TV, Game Consoles, etc.
I probably left out something but hey, I am far from being perfect, and just in case, here is a mind boggling schema for you to chew on.
It is old but it gives you an idea of the complexity of advertising online.
Otherwise, how about this other one? If you have been in London or Paris trying to get from one place to another using the subway, you’ll love it. Only thing here is that when advertising online you need to take several trains at the same time.
The point here is that with the 7 Ps, at the very least we have done the minimum to ensure that we have a chance to succeed with our marketing plan.
However, when it comes to implementing this on the web the real unknown is what channels to choose? A/B testing of the message is great but which channel should we start on? Do we focus on SEO (I call it the “VOODOO Technology), PPC, SEM, Social? They are all great but then again, trying to launch a campaign on all the platforms available would cost a fortune.
In addition, should you go for advertising on social networks would you select Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok or one of the myriad of other social networks popping up on a monthly basis. What about SEM? Google is king but pricing is way.. way.. up there. Is Bing an option? Yes, but prices are not much better. Is there other search options like Firefox, DuckDuckGo, Wiki, etc. The problem here is that most of their advertising revenues are generated from Google or BING redirect. So much for that.
Bottom line as far as I am concerned is to be able to 1) KNOW YOUR CUSTOMER or at least have a target audience and buyers in your scope and 2) BE PATIENT and try, try and try. Unless you have Nike of the Ford Motor company advertising budget you have no option but to start with a specific and narrow path to your online advertising (and they probably spend 50% or more of their budget on wasted ads campaigns and promotions let alone agency costs, but they can afford it).
To have a chance to a breakthrough, use your judgement, creativity and be a good neighbor by giving part of what you make to charity or a social program that is in line with your audience. They will love it. Call on your customers to become your sales force by offering incentives and above all spend your energy on customer service and support. Amazon will take back any orders that you return without questions for a simple reason. This is probably the most effective marketing strategy they have implemented. We buy Amazon and keep on going back because they will take back my order if I change my mind, no questions asked.
Does Amazon know my habits and A/B test offers or analyze the heck out of what I do to try to sale me other stuff? You bet. However, their primary attraction is that I find what I want there and I know that I can return it 99.9% of the time. Price is key of course but the choice between Amazon and another unknown site or even e-bay or Walmart for example is a no brainer. Amazon wins my business. By the way that does not mean that they are great at what they do as far as analytics. For instance, how many times have you done a search on Amazon and bought something only to see this same item appearing as an option to buy from them on a search engine? Yea, they too are far from perfect in their analytic.
Marketing is not something that you can achieve with great success unless you spend the time to analyze what your product is, what it offers, who it is best suited for and how you can best service your customers. Only then can you start thinking of channels of advertising.
If you need some expert input, there are a myriad of consultants and so-called marketing “guru” that you can hire to help you with your marketing. For my part, I like to offer a free consultation to first assess the needs of potential customers. The reason I do this is not to “hook” them with promises of a rosy future and a juicy. Rather I want to assess for myself what is in place and, more importantly, how realistic this potential client is. Someone with unrealistic expectation is worst than not having a client in my view and I would rather pass.
To conclude, here are some pointers that I like to give to my clients.
- Messaging and packaging: Know your audience true motive for buying something and tailor your message to appeal to their need. Note that it may be material but also and probably even more emotional.
- Make several versions of this message and “shop” it around to people you know or existing clients. Ideally people in the same demographic as your targeted customers and/or using the same approach to searching and buying.
- Select a channel that is the most promising for your product or service. It may not be the most “popular” but it is one where your competitors may have a presence and where you want to test your message. Find out via simple search on these platforms
- Make sure that you have an incentive to invite first time buyers to re-order. Make them come back to buy again with a coupon, BOGO offer or point and reward system or anything that you may have to insure a second, third and more orders. I do not recommend cross selling another company’s product.
- Offer Free, no question asked, return policy. Perhaps you may be tempted to charge for return shipping cost but don’t. Incorporate this in your cost of doing business.
- If you have a customer support Chat make sure that it works and that the automated responses that are provided are continually update and that you have someone ready to take over if answers are not adequate. Otherwise offer a call option and be clear about hours of operation. Less expensive is to offer email support but make sure they answer request within 48 hours.
- Create a newsletter and send email offers regularly with incentives, coupons, special offers to keep your customer interested and wanting to see more as opposed to adding your email to the junk file.
- Create and send survey with some type of reward for whomever completes it. This is invaluable information that will help you better understand your customers and their needs and expectations as well as pointing out issues you may have. However, do not over do it and load a single survey with tons of questions.
- Put in place the analytic tools that you need to better understand how your traffic performs and which channels brings in the best ROI. Here too, do not overdo it and over analyze everything. Analytic is a simple tool to provide basic information on what works and what does not. Keep it that way.
- Do it all other again when you start a new marketing campaign or a new advertising campaign or introduce a new service or product. Do it all over again even if you are selling the same thing or offering the same service, just to make sure that the channels you used the past six months are still as good today.
There are probably more things you can do but these are the main points that I can highlight. However, one thing is for certain. The Devil is in the detail so implementation and staying on message and focus are paramount to most anything else.
I hope all this helps.
* The 7 Ps of marketing (business.qld.gov.au)
The 7 Ps are a set of recognized marketing tactics, which you can use in any combination to satisfy customers in your target market. The 7 Ps are controllable, but subject to your internal and external marketing environments. Combining these different marketing tactics to meet your customers’ needs and wants is known as using a ‘tactical marketing mix’.
Product
Product refers to what you are selling, including all of the features, advantages and benefits that your customers can enjoy from buying your goods or services. When marketing your product, you need to think about the key features and benefits your customers want or need, including (but not limited to) styling, quality, repairs, and accessories.
You can use research and development to inform the development of new products in your business.
Price
This refers to your pricing strategy for your products and services and how it will affect your customers. You should identify how much your customers are prepared to pay, how much mark-up you need to cater for overheads, your profit margins and payment methods, and other costs. To attract customers and retain your competitive advantage, you may also wish to consider the possibility of discounts and seasonal pricing.
Learn more about pricing your products.
Promotion
These are the promotional activities you use to make your customers aware of your products and services, including advertising, sales tactics, promotions and direct marketing. Generally these are referred to as marketing tactics.
Learn more about promotional activities.
Place
Place is where your products and services are seen, made, sold or distributed. Access for customers to your products is key and it is important to ensure that customers can find you.
You can set yourself apart from your competition through the design of your retail space and by using effective visual merchandising techniques. If you are not a retail business, place is still an important part of your marketing. Your customers may need a quick delivery turnaround, or want to buy locally manufactured products.
If you are starting a new business, finding the right business location will be a key marketing tactic.
People
People refer to the staff and salespeople who work for your business, including yourself.
When you provide excellent customer service, you create a positive experience for your customers, and in doing so market your brand to them. In turn, existing customers may spread the word about your excellent service and you can win referrals.
Give your business a competitive advantage by recruiting the right people, training your staff to develop their skills, and retaining good staff.
Process
Process refers to the processes involved in delivering your products and services to the customer. It is also about being ‘easy to do business with’.
Having good process in place ensures that you:
repeatedly deliver the same standard of service to your customers
save time and money by increasing efficiency.
Learn more about business processes, procedures and standards.
Physical evidence
Physical evidence refers to everything your customers see when interacting with your business. This includes:
the physical environment where you provide the product or service
the layout or interior design
your packaging
your branding.
Physical evidence can also refer to your staff and how they dress and act.
Consider how your store’s layout, fixtures and signage can build your brand and increase your sales.
Also consider…
Find out how to develop your staff through mentoring.
Learn how to improve you and your staff’s sales skills.